If you’ve ever tried scraping Amazon (or any other e-commerce site), you know that the main challenge is that product pages can vary widely in structure. That makes programmatic data parsing tricky, as you have to account for many edge cases.
On top of that, almost all e-commerce platforms implement anti-bot measures, like Amazon’s infamous CAPTCHA:
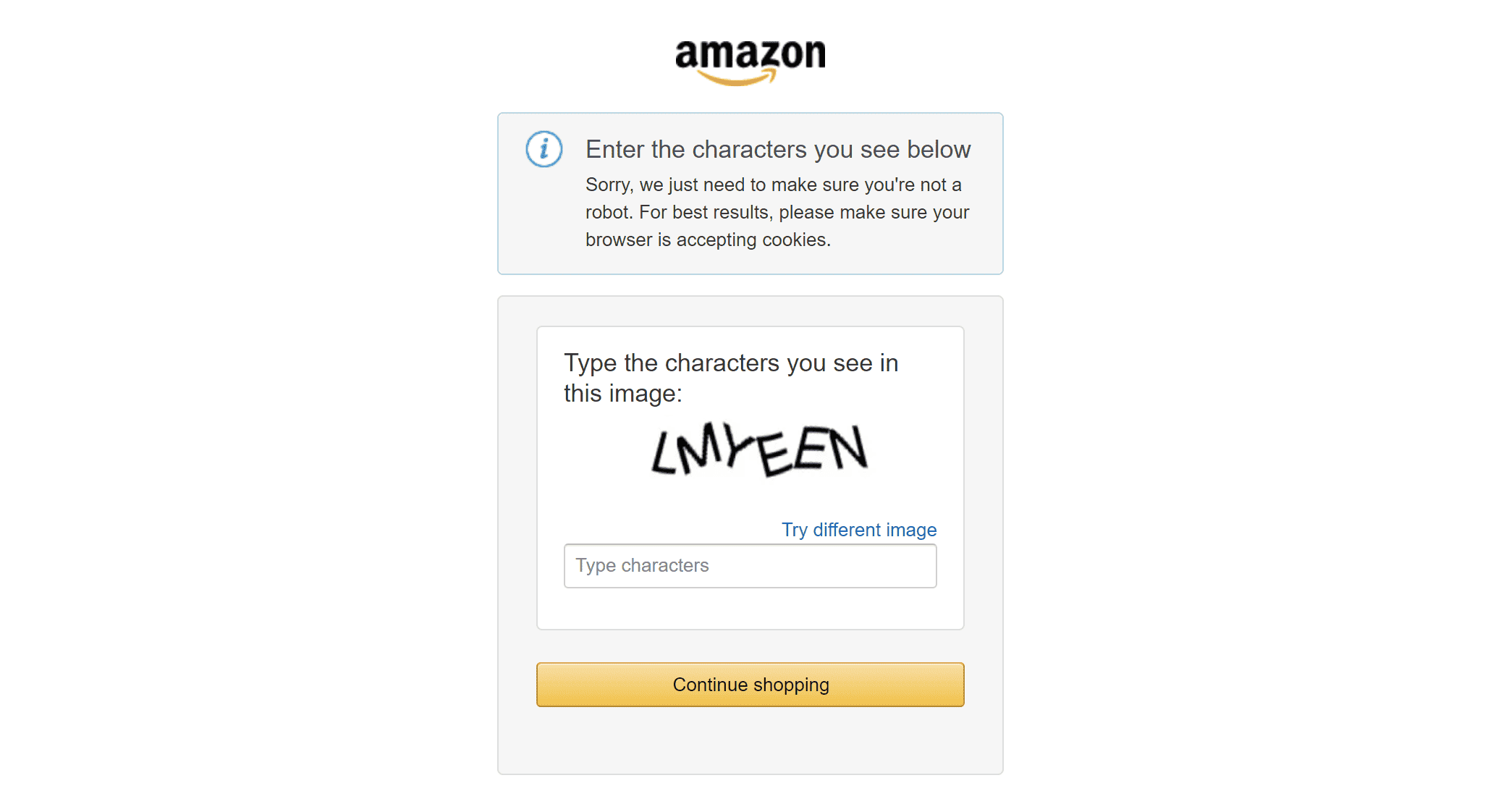
These challenges are engineered to block automated scraping of public data. The best way to overcome them is by using a unified e-commerce scraping solution that can extract various types of data – products, sellers, reviews, and more – from complex e-commerce platforms like Amazon through a single, consistent interface.
This solution is called E-commerce Scraping Tool:
This is an Actor on Apify Store designed for scraping data from e-commerce websites.
Among the data fields it can scrape are:
- Product name
- Product description
- Price and currency
- Product identifiers: SKU, MPN, GTIN (EAN, UPC, ISBN)
- Brand
- Image URL
- Product variants (where available)
- Product URL
Let's take a look at the scraping process.
How to collect Amazon prices via Python API using E-commerce Scraping Tool
In this detailed guide, you’ll learn how to use E-commerce Scraping Tool to collect Amazon product prices via API in a Python script.
Here's our workflow:
- Set up a Python project
- Access the Actor
- Get started with the API integration
- Prepare your script to get Amazon prices via Python API
- Get and set your Apify API token
- Configure the Actor
- Complete code
- Test the Amazon scraping script
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, make sure you have:
- An Apify account
- A basic understanding of how Apify Actors work when called via API
- Python 3.10+ installed locally
- A Python IDE (e.g., Visual Studio Code with the Python extension or PyCharm)
- Familiarity with Python syntax and the HTTP request mechanism
1. Set up a Python project
If you don’t already have a Python project set up, follow the steps below to create one. Start by creating a new folder for your Amazon price scraper:
mkdir amazon-price-scraper
Next, navigate to the folder and set up a virtual environment inside it:
cd amazon-price-scraper
python -m venv .venv
Open the project in your Python IDE and create a new file named scraper.py. That's where you’ll write your API-based e-commerce scraping logic.
To activate the virtual environment on Windows, execute this command in the IDE's terminal:
.venv\Scripts\activate
Equivalently, on Linux/macOS, run:
source .venv/bin/activate
2. Access the Actor
To begin your journey of collecting Amazon data via API with E-commerce Scraping Tool, start by logging into your Apify account. Then, open Apify Console and select Apify Store from the menu on the left:
On Apify Store, search for "e-commerce scraping tool,” and select E-commerce Scraping Tool:

You’ll be redirected to the Actor page:
3. Get started with the API integration setup
It’s time to set up E-commerce Scraping Tool for API usage. Begin by locating the API dropdown in the top-right corner. Then, select API clients:
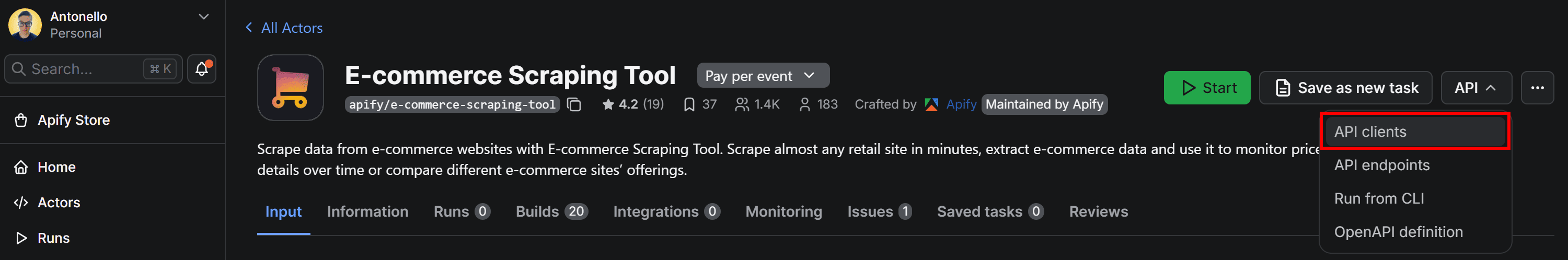
This will bring up a modal with ready-to-use code snippets for interacting with the Actor via the Apify API client. By default, it displays a Node.js snippet, so switch to the Python tab:
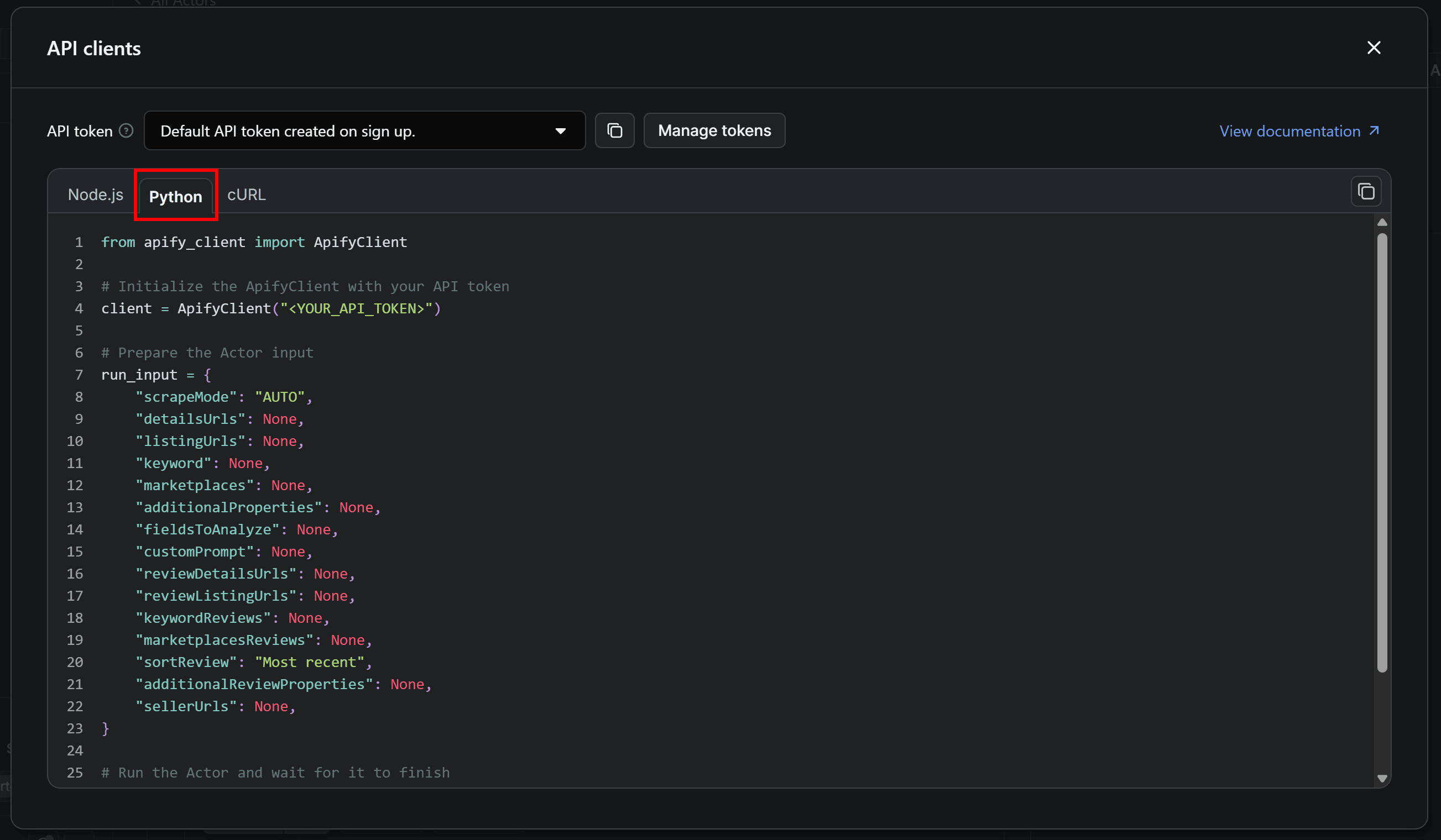
Copy the Python snippet from the modal and paste it into your scraper.py file. Keep the modal open, as we’ll refer back to it in a next step.
4. Prepare your script to get Amazon prices via Python API
If you take a close look at the snippet in the “API clients” modal, you’ll surely notice that it relies on the apify_client Python library:
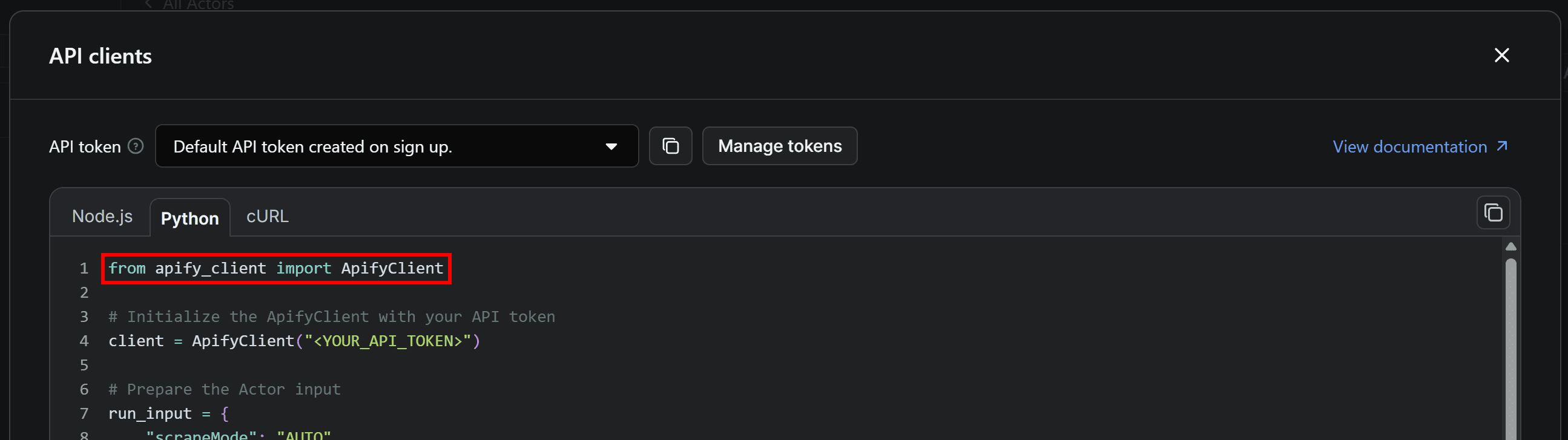
To install apify_client in your Python projects, execute this command in the activated virtual environment:
pip install apify_client
In the snippet, you can also see a placeholder for your Apify API token (the "YOUR_API_TOKEN>" string). That token is required to authenticate API calls through the Apify API client.
Now, the best practice is to never hard-code secrets like that directly in your code. On the contrary, you should read them from environment variables. To simplify this process, we’ll employ the python-dotenv library, which lets you load environment variables from a .env file.
Install python-dotenv in your activated environment:
pip install python-dotenv
Next, create a .env file in the root folder of your project. Your folder structure should look like this:
amazon-price-scraper/
├── .venv/
├── .env # <-----
└── scraper.py
Inside the .env file, add the APIFY_API_TOKEN environment variable:
APIFY_API_TOKEN="YOUR_APIFY_API_TOKEN"
For now, "YOUR_APIFY_API_TOKEN" is just a placeholder, but you’ll soon replace it with your actual Apify API token.
Then, update scraper.py to load environment variables and read the token:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
# Load environment variables from the .env file
load_dotenv()
# Retrieve the required API token from environment variables
APIFY_API_TOKEN = os.getenv("APIFY_API_TOKEN")
The load_dotenv() function reads variables from the .env file, and os.getenv() retrieves them in your script.
Finally, pass the API token value to the ApifyClient constructor:
client = ApifyClient(APIFY_API_TOKEN)
Your scraper.py script is now set up to connect to E-commerce Scraping Tool via authenticated API calls.
5. Get and set your Apify API token
The next step is to retrieve your Apify API token and add it to your .env file. That completes the setup required for Amazon scraping via API integration with the E-commerce Scraping Tool.
Back to the E-commerce Scraping Tool Actor’s page, in API clients modal, click the Manage tokens button:
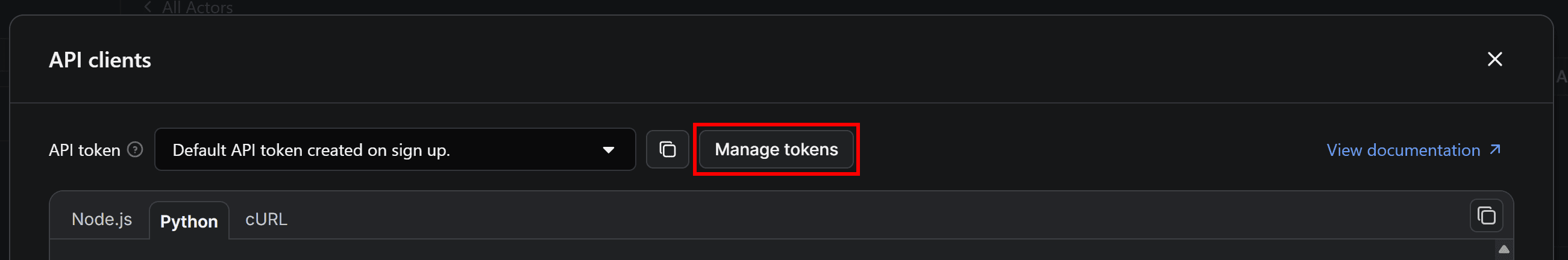
You’ll reach the API & Integrations section of the Settings page of your Apify account. To access your Apify API token, press the Copy to clipboard icon next to the Default API token created on sign up entry:
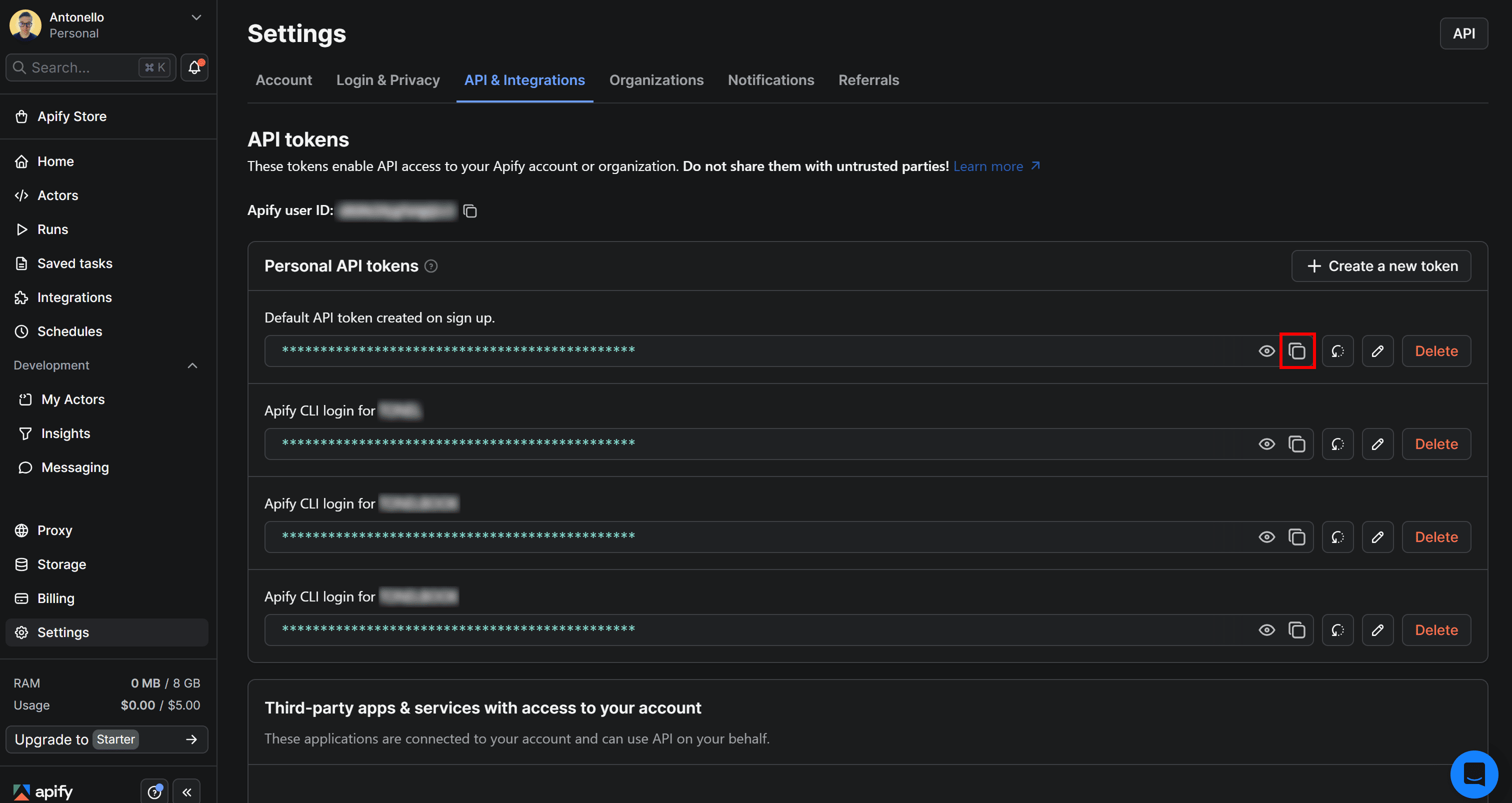
Finally, paste the API token into your .env file like this:
APIFY_API_TOKEN=PASTE_YOUR_TOKEN_HERE
Replace the PASTE_YOUR_TOKEN_HERE placeholder with the actual token you just copied.
6. Configure the Actor
Like any other Actor, E-commerce Scraping Tool requires the correct input parameters to retrieve the desired data. When using the ApifyClient, these parameters specify which pages the Actor should scrape via API.
In this example, the target website is Amazon. So, assume you want to scrape prices from the following product pages:
https://www.amazon.com/Hanes-Pullover-EcoSmart-Fleece-Hoodie/dp/B00JUM36Rhttps://www.amazon.com/Microfiber-Cleaning-Cloth-Performance-Washes/dp/B08BRJHJF9
To simplify the input configuration process, open the Input section on the Actor’s page. Visually interact with the Product detail URLs field, and paste the two target URLs:
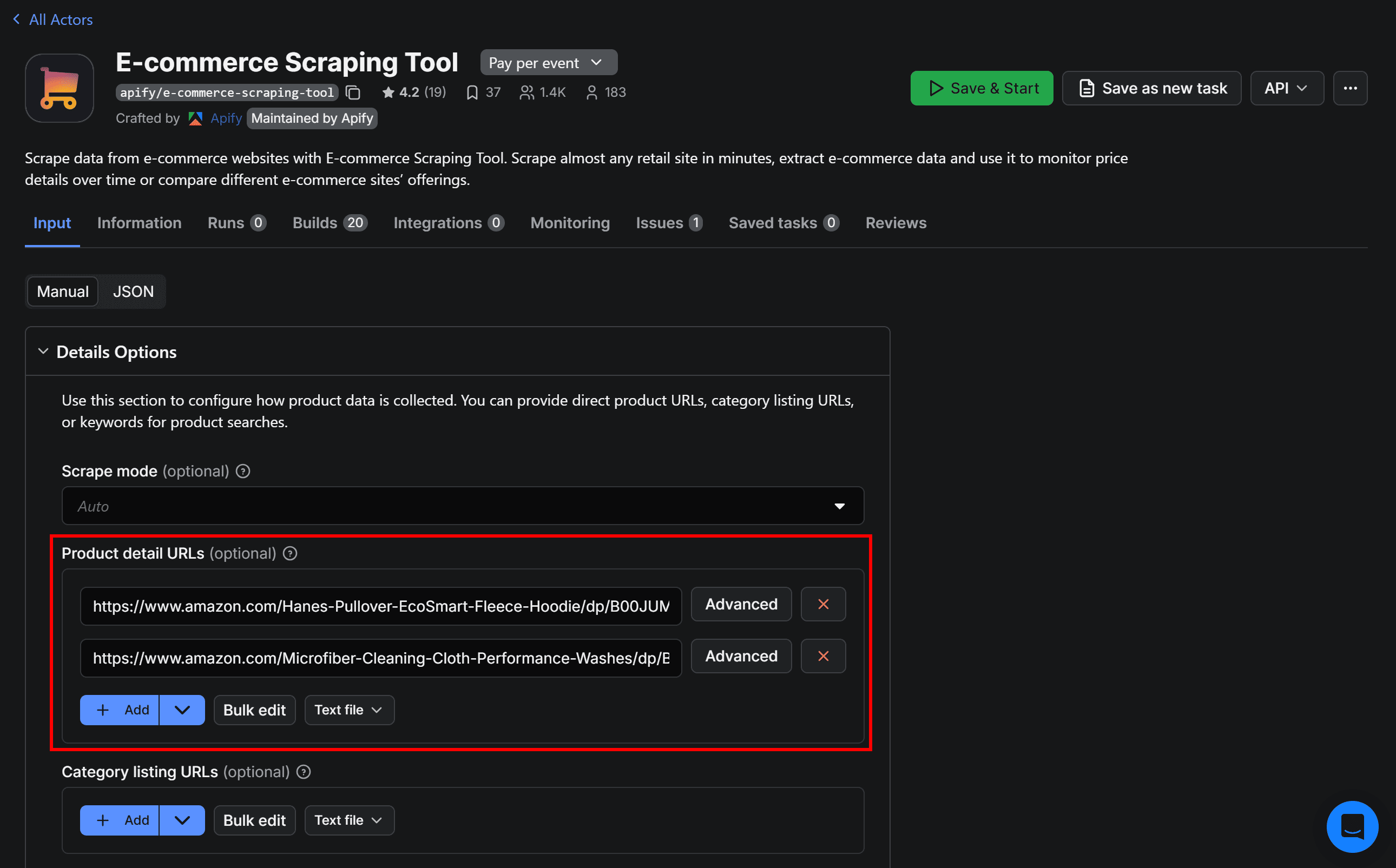
Then, switch to the JSON view:
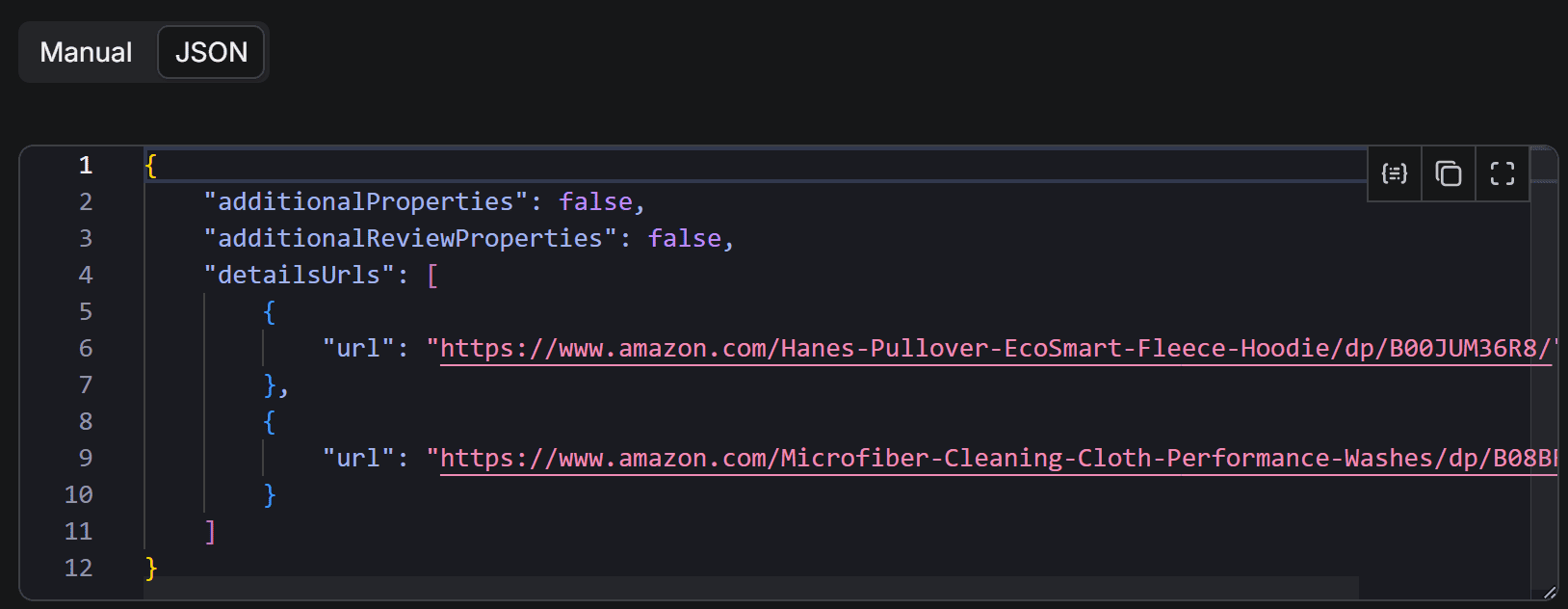
You’ll notice that the two URLs appear in the detailsUrls array. Following that structure, populate the input dictionary in Python and call E-commerce Scraping Tool as shown below:
run_input = {
"scrapeMode": "AUTO",
"detailsUrls": [
{
"url": "https://www.amazon.com/Hanes-Pullover-EcoSmart-Fleece-Hoodie/dp/B00JUM36R8"
},
{
"url": "https://www.amazon.com/Microfiber-Cleaning-Cloth-Performance-Washes/dp/B08BRJHJF9"
}
]
}
run = client.actor("2APbAvDfNDOWXbkWf").call(run_input=run_input)
This configuration ensures the Actor is properly set up to scrape data from the specified product pages.
7. Complete code
Below is the final code of your Amazon price scraper:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from apify_client import ApifyClient
# Load environment variables from the .env file
load_dotenv()
# Retrieve the required API token from environment variables
APIFY_API_TOKEN = os.getenv("APIFY_API_TOKEN")
# Initialize the ApifyClient using your Apify API token
client = ApifyClient(APIFY_API_TOKEN)
# Set up the input for the E-commerce Scraping Tool to scrape Amazon products
run_input = {
"scrapeMode": "AUTO",
"additionalProperties": True,
"detailsUrls": [
{
"url": "https://www.amazon.com/Hanes-Pullover-EcoSmart-Fleece-Hoodie/dp/B00JUM36R8"
},
{
"url": "https://www.amazon.com/Microfiber-Cleaning-Cloth-Performance-Washes/dp/B08BRJHJF9"
}
]
}
# Execute the E-commerce Scraping Tool and wait for the scraping process to complete
run = client.actor("2APbAvDfNDOWXbkWf").call(run_input=run_input)
# Retrieve and print the Amazon product data from the run’s dataset (if available)
for item in client.dataset(run["defaultDatasetId"]).iterate_items():
print(item["offers"])
Note that this prints only the offers field of the returned product data object. That’s where the price is stored and contains price data in a structure like this:
{
"price": "€32.49",
"priceCurrency": "EUR"
}
The price information includes both the amount and its currency in separate fields.
Thanks to Apify’s E-commerce Scraping Tool, you can build an API-based Amazon price scraper in just around 35 lines of Python code. Let's put it into action.
8. Test the Amazon scraping script
Open your terminal and run the Amazon scraping script with:
python scraper.py
The script will connect to the configured Actor and return two objects - each one contains the scraped product information. Here’s the first result, corresponding to the price of the first target product:
{
"price": "$8.92",
"priceCurrency": "USD"
}As you can verify, the scraped price matches what appears on the Amazon product page:
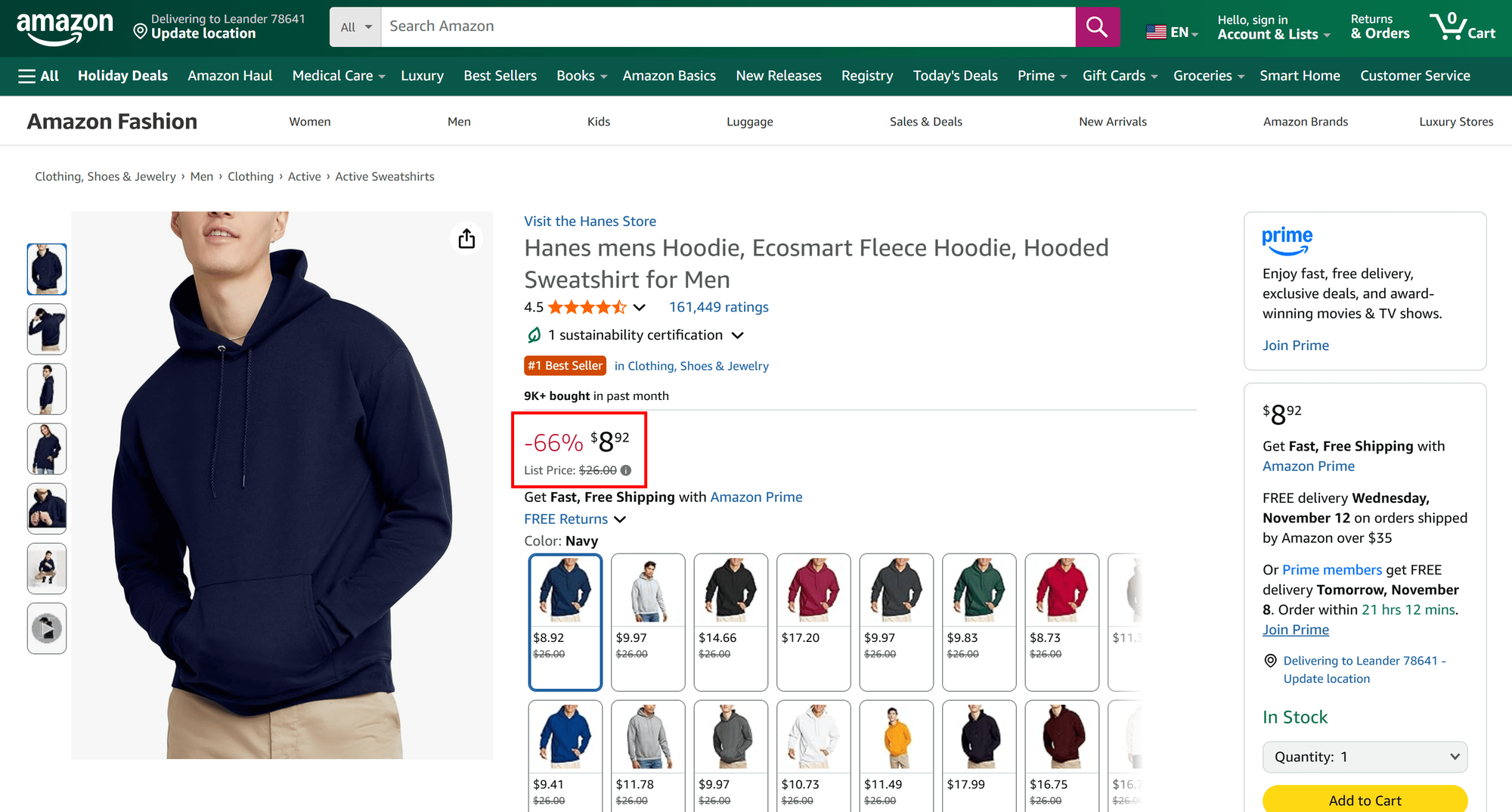
Next, take a look at the price for the second target product:
{
"price": "$8.98",
"priceCurrency": "USD"
}
Again, the extracted price matches the actual product page:
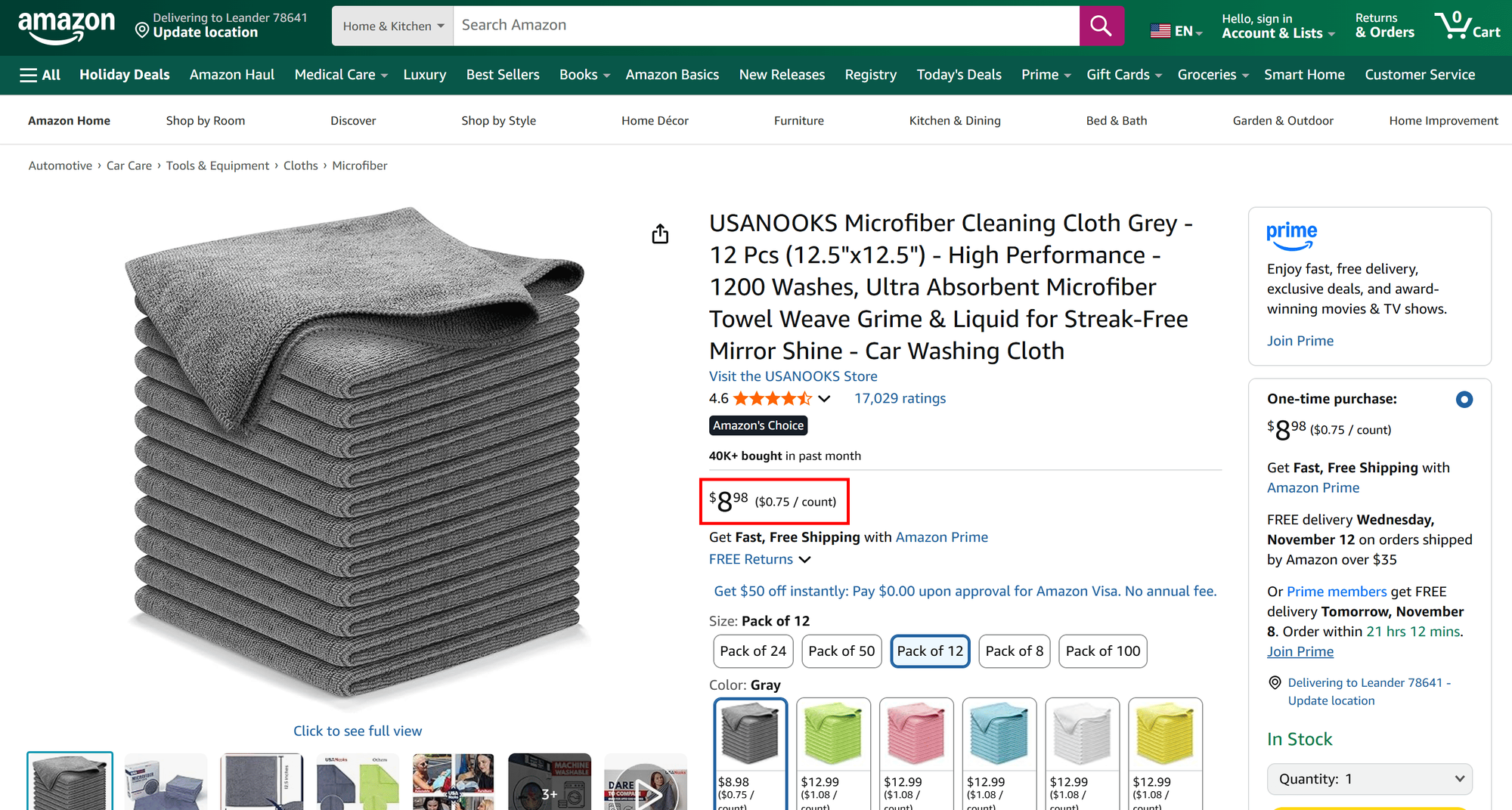
Your Amazon price scraper is now up and running successfully.
Next step: Collect different types of data
Now that your Amazon price scraper is operational, you can play with the input settings to collect more detailed or different types of data.
To further expand the scraped data, explore other input options supported by E-commerce Scraping Tool:
| Parameter Name | Key | Type | Description | Value Options / Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scrape mode | scrapeMode | Enum | Defines how data should be scraped: via browser rendering, lightweight HTTP requests, or automatically chosen mode. | "AUTO" (default), "BROWSER", "HTTP" |
| Product detail URLs | detailsUrls | Array | Direct URLs to individual product detail pages. | — |
| Category listing URLs | listingUrls | Array | URLs to category or listing pages containing multiple products. | — |
| Keyword for search | keyword | String | Keyword used to search for products across marketplaces. | — |
| Marketplaces for keyword search | marketplaces | Array | Marketplaces where the keyword search should be performed. | — |
| Include additional properties | additionalProperties | Boolean | Includes extra product-related properties in the result. | — |
| AI summary – data points | fieldsToAnalyze | Array | Data points to pass to AI for generating a summary. | — |
| AI summary – custom prompt | customPrompt | String | Custom AI prompt for processing data points; default prompt used if not provided. | — |
| Review detail URLs | reviewDetailsUrls | Array | Direct URLs to product detail pages for extracting reviews. | — |
| Review listing URLs | reviewListingUrls | Array | URLs containing multiple product reviews to be scraped. | — |
| Keyword for reviews | keywordReviews | String | Keyword used to search for product reviews across marketplaces. | — |
| Marketplaces for review search | marketplacesReviews | Array | Marketplaces where review keyword searches are performed. | — |
| Review sort type | sortReview | Enum | Defines how product reviews should be sorted; falls back to default if unsupported. | "Most recent" (default), "Most relevant", "Most helpful", "Highest rated", "Lowest rated" |
| Include additional review properties | additionalReviewProperties | Boolean | Includes extra review-related properties in the response. | — |
| Seller profile URLs | sellerUrls | Array | Direct URLs to seller or store profile pages for extracting seller info. | — |
The benefits of using E-commerce Scraping Tool
The ten main benefits of using E-commerce Scraping Tool for price data extraction:
- All-in-one e-commerce scraper: Collect structured product, pricing, and inventory data from major retailers, marketplaces, and catalogs via the same interface.
- Broad platform coverage: Supports scraping global and regional e-commerce platforms such as Amazon, Walmart, eBay, Alibaba, Target, Flipkart, MercadoLibre, Lidl, Alza, Decathlon, Rakuten, and more - even across multiple sites in a single run to support product comparison or data enrichment scenarios.
- Flexible input options: Scrape data from individual product URLs, category pages, listing pages, or via keyword-based searches. All that through a single tool.
- Cloud execution: Run scraping jobs in the cloud without worrying about local environment setup, ensuring high scalability and reliability.
- Anti-bot and CAPTCHA handling: Built-in mechanisms bypass anti-bot protections and CAPTCHAs, keeping your scraping process smooth and uninterrupted.
- Integrated proxy management: Built-in support for rotating residential and data center proxies to avoid IP bans and geographical restrictions.
- AI-enhanced data processing: Possibility to summarize product information, analyze trends, or generate insights automatically using AI-driven prompts.
- Multiple export formats: Retrieve data as JSON, CSV, Excel, or HTML, allowing easy integration with existing pipelines or analytics tools.
- Customizable scraping modes: Choose between
HTTP,Browser, orAutomodes depending on your target site and required data depth. - Scheduler support: Automate regular e-commerce scraping tasks to keep your data fresh without manual intervention.
Conclusion
Using E-commerce Scraping Tool eliminates the need to build and maintain your own scraping scripts.
Although this example focused on prices, E-commerce Scraping Tool can handle multiple use cases: You can use it to gather a wide range of product information, including reviews, seller details, and more.
Discover the full capabilities of this Actor and use the Apify SDKs to enhance and automate your e-commerce data workflows.
FAQ
Why prefer E-commerce Scraping Tool over the Amazon Scraper Actor?
E-commerce Scraping Tool supports multiple e-commerce platforms from the same interface, ideal for data comparison and enrichment use cases.
Why use an API-based approach to Amazon price scraping?
This approach ensures reliable, structured, and consistent data retrieval. With a cloud-based solution like E-commerce Scraping Tool, you don’t need to worry about website layout changes or anti-bot protections, as these challenges are managed automatically for you.
Is targeting Amazon product pages through E-commerce Scraping Tool legal?
Yes, scraping Amazon product pages is legal, as it only accesses publicly available data. Check out Is web scraping legal? for more details.