If you’re planning to expand to new markets, you need data. Google Maps is one of the easiest ways to explore local markets, find competitors, and discover new business opportunities. However, it wasn’t built for collecting data at scale:
- Search results usually cap at around 120 listings, which means you have to keep zooming into smaller map sections just to uncover more places.
- There’s no built-in way to export data in bulk, so teams often end up copying details manually.
- The official API doesn’t fully solve this either - it returns limited results per request, requires constant usage monitoring to avoid hitting quotas, and its pricing or restrictions can change without warning.
Using a web scraping tool removes these bottlenecks by automatically collecting structured business data - names, websites, ratings, reviews, hours, and more - across thousands of Google Maps queries.
Instead of spending hours gathering listings, you can get clean datasets ready for market expansion analysis, competitive research, or growth workflows. The JSON export also lets you feed the data directly into AI tools without additional cleanup.

Market expansion analysis using scraped data
How to conduct a market expansion analysis with Google Maps Scraper
We’re going to show you how to use the Apify platform and Google Maps Scraper to extract data from Google Maps.
This scraper will enable you to extract the most recent data directly from the website, including reviews, ratings, business details, and popular times. It also bypasses Google Maps’ search limits to capture more than 120 results and scales to thousands of places without manual effort.
Step 1. Go to Google Maps Scraper
Go to Google Maps Scraper. If you don’t have an Apify account yet, you’ll be prompted to create one for free. You’ll access Apify Console, a workspace for running and building web automation tools.

Step 2. Configure the scraper and run it
Once you have your account set up, head to the scraper’s input tab. There are two ways to get your Google Maps data: either by using search terms or URLs. For the purpose of this tutorial, we’ll use two search terms as input: gym and fitness center.
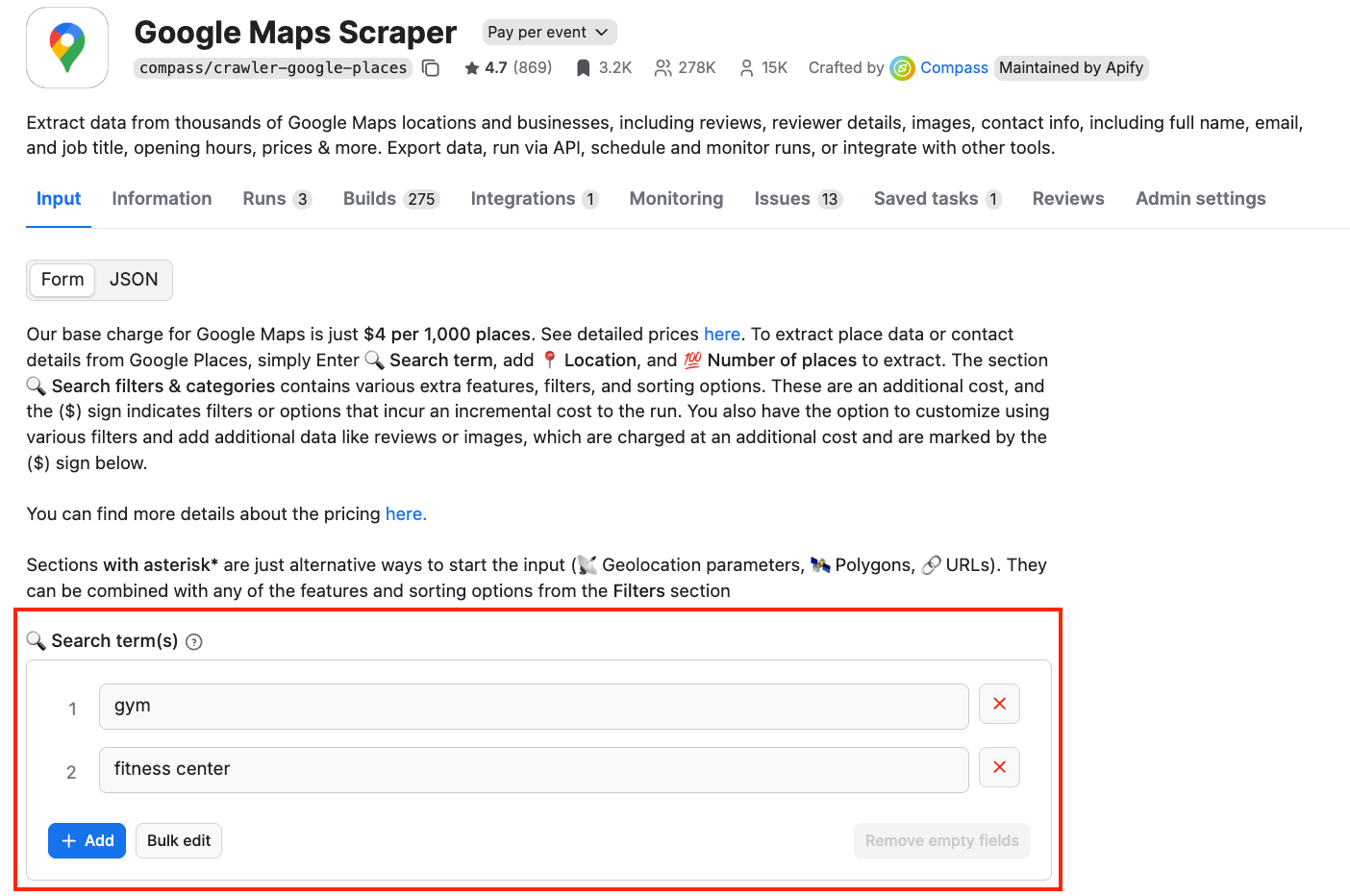
Now we also need a location we want to scrape data from. There are many different ways to customize your search - you can either choose the entire city or create geolocation parameters. We want to compare the market potential in three German cities, so we’ll run three scraping sessions for Berlin, Munich, and Frankfurt. Note that you can use only one location per session.
Let’s start with changing the country and the city in the Define the search area by other geolocation parameters field.
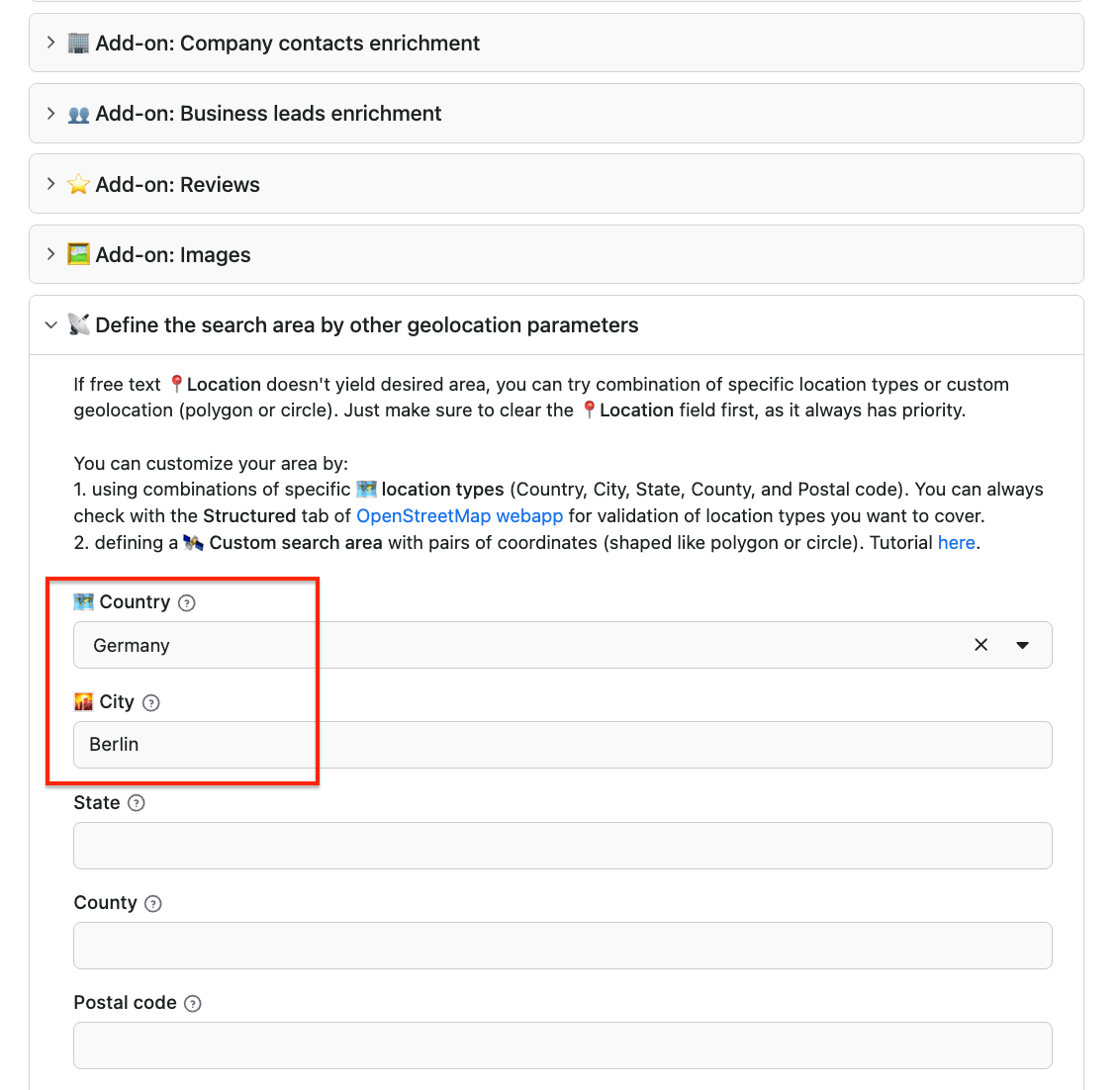
This scraper offers add-ons and filters to further enrich your datasets. With the Company contacts enrichment add-on, the scraper doesn’t just pull business listings - it also uncovers contact details from the company’s website. This can include emails, phone numbers, and links to social media accounts.
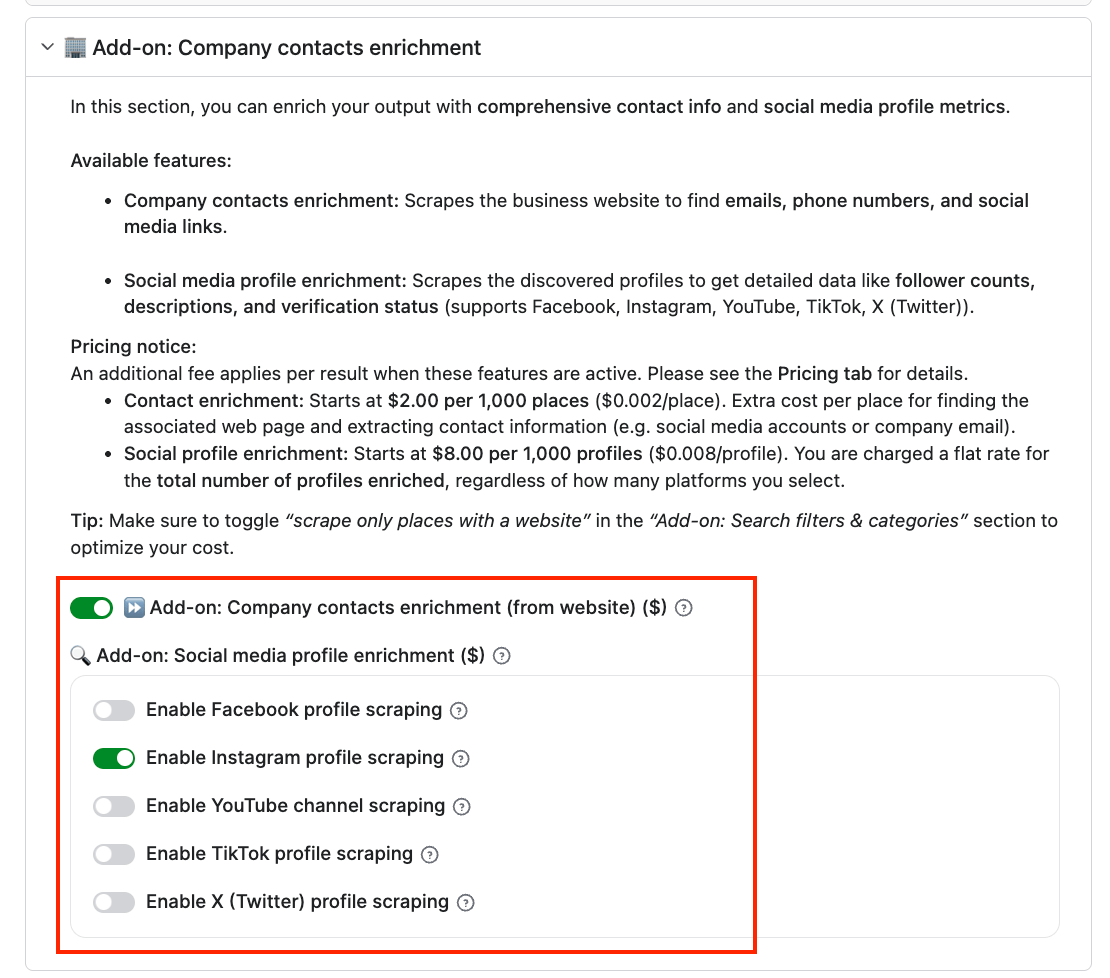
With the Business leads enrichment feature, you can tap into a broader database of employee data, providing insights such as headcount, staff names, and other business details. You can even filter by department, e.g. C-Suite, HR, or Product.
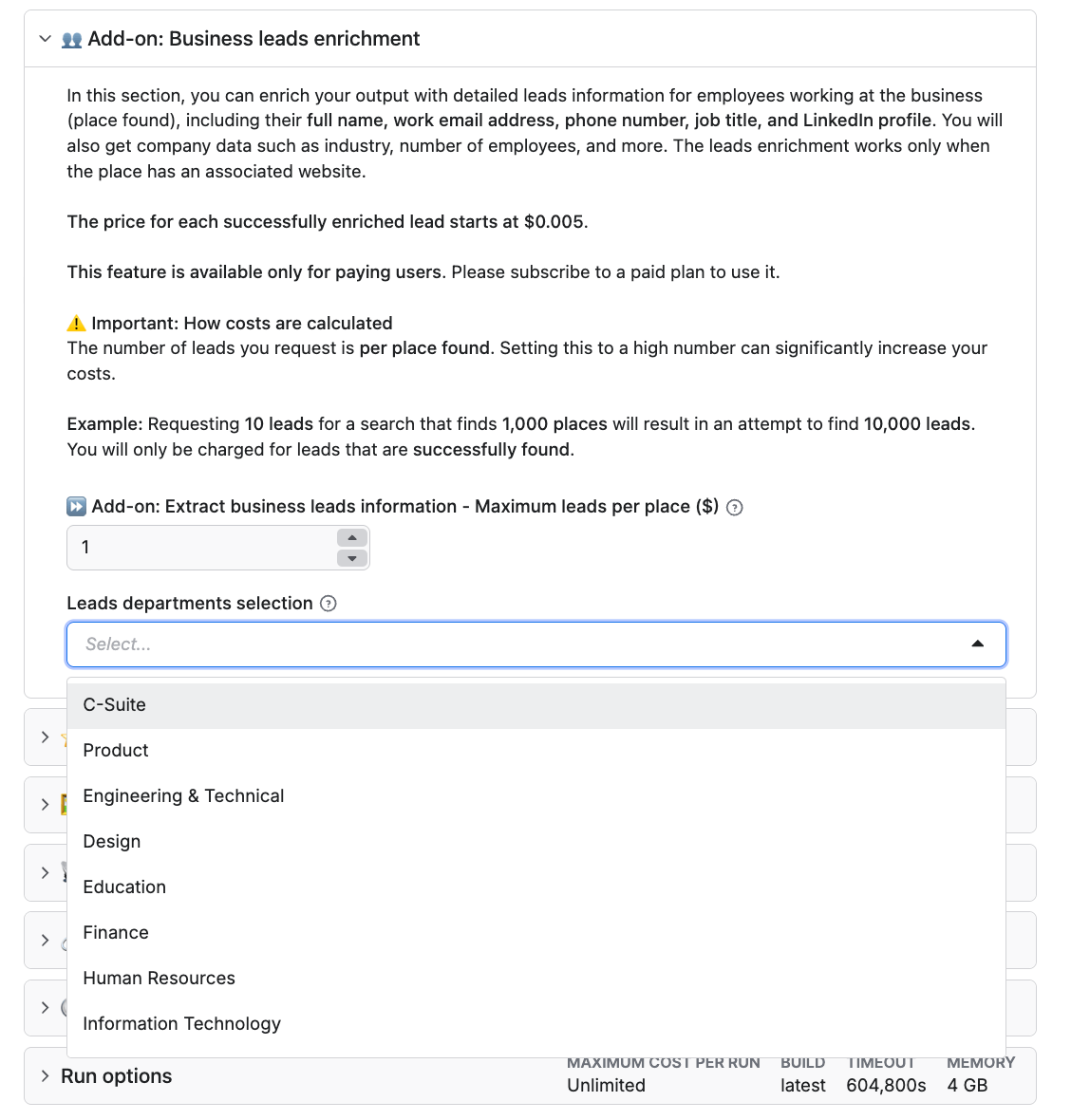
Google Maps Scraper can also extract reviews. Select the add-on to do that. Note that personal data extraction about reviewers is also possible, but has to be explicitly enabled in the input.
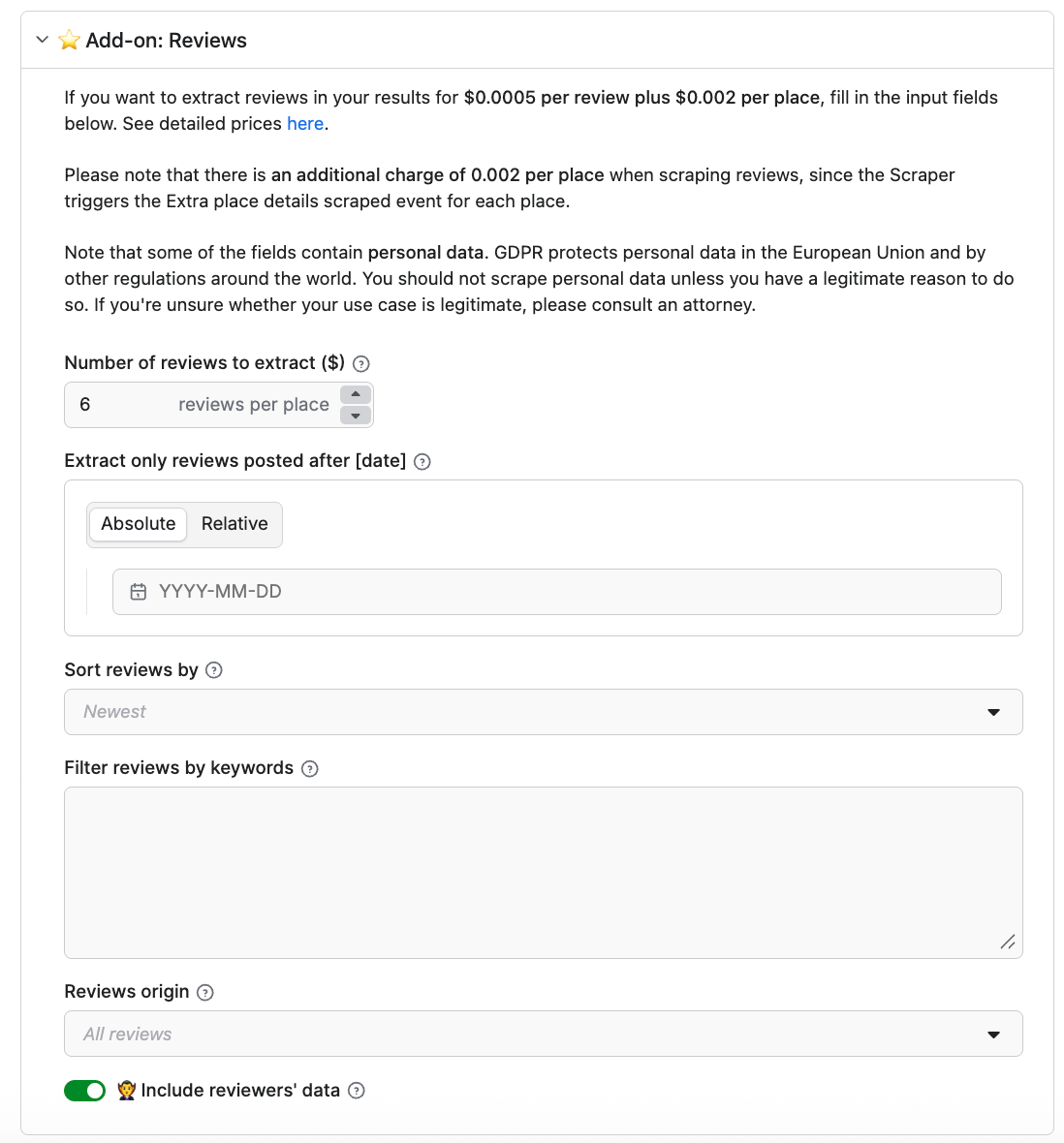
Once you’re happy with your configuration, click Save & Start to run the scraper.
Step 3. Get your results
After the scraper finishes running, you can check your results in the preview table. In this example, it took only 4 minutes to collect detailed information about 90 gyms and fitness centers in Berlin - including reviews, star rating, websites, contact details, and much more.
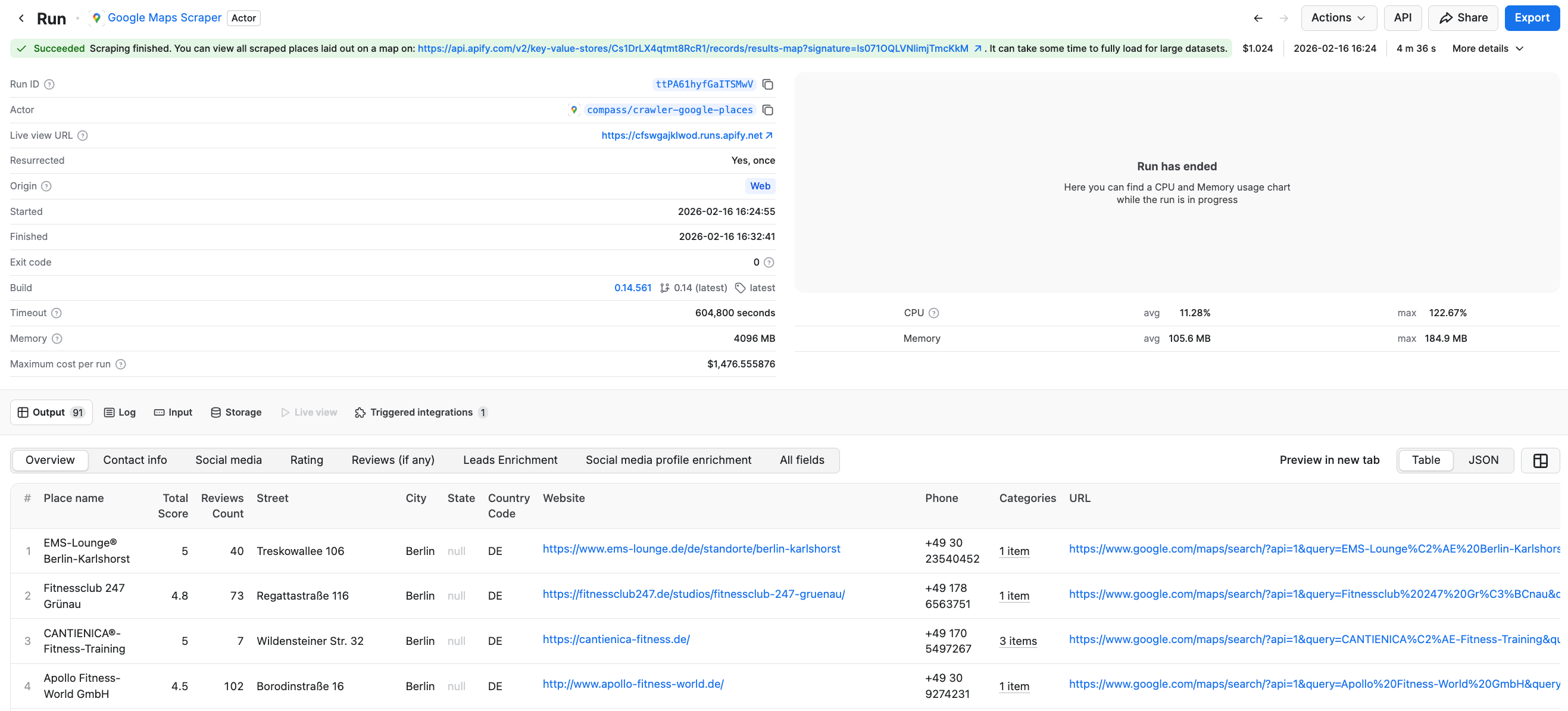
Click the Export button to get your results in a format of your choosing - JSON, CSV, Excel, XML, and more, depending on your data analysis workflow. You can also select or omit fields to reduce the information noise. We’ll download the datasets as JSON files.
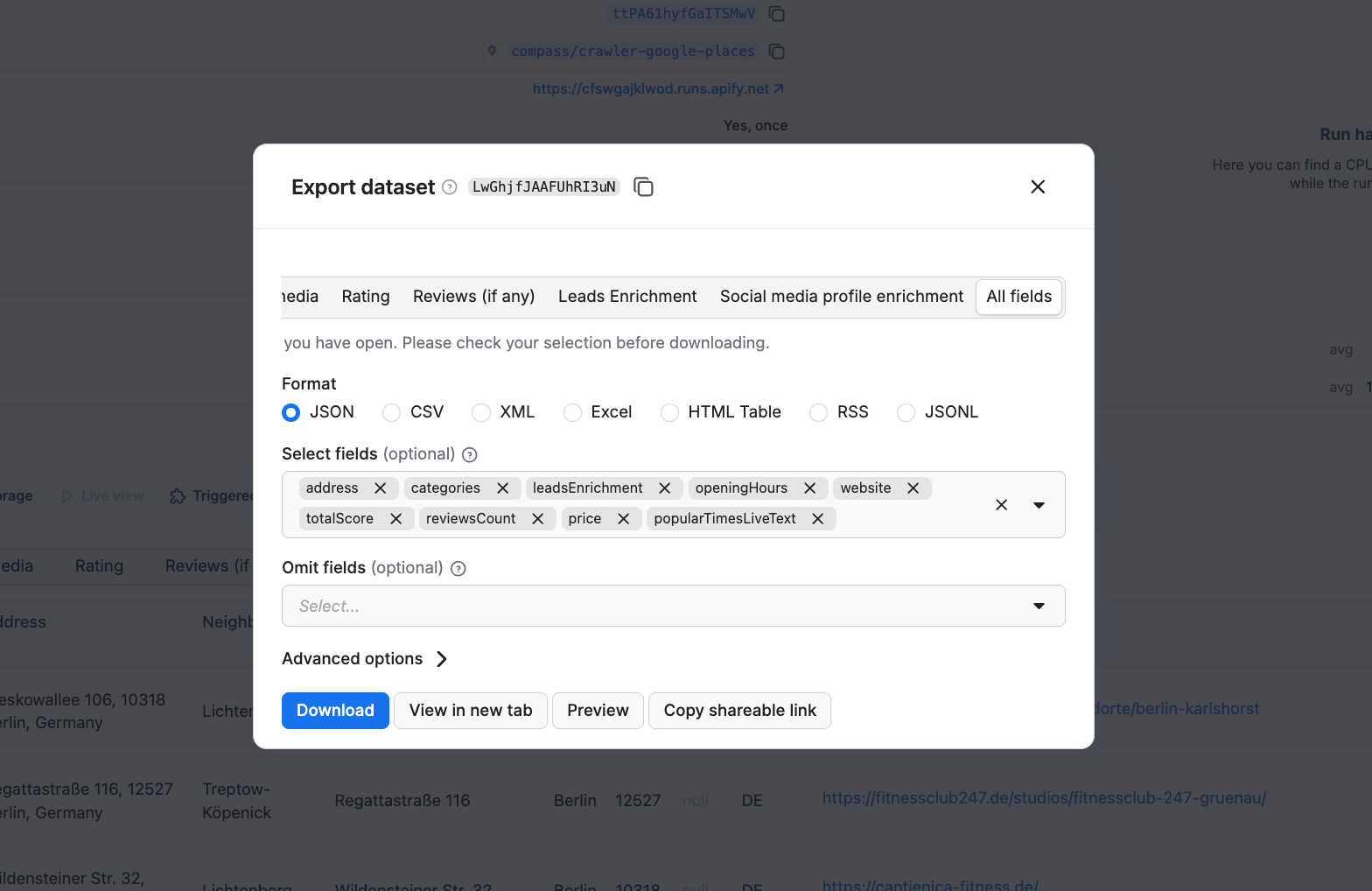
To create a market expansion analysis across German cities, we’ll run the scraper two more times, changing the location to Munich and then Frankfurt, leaving other parameters unchanged.
Step 4. Conduct a market expansion analysis
If you don’t have a team of analysts at your disposal, you can still create a reliable data analysis yourself, using AI tools.
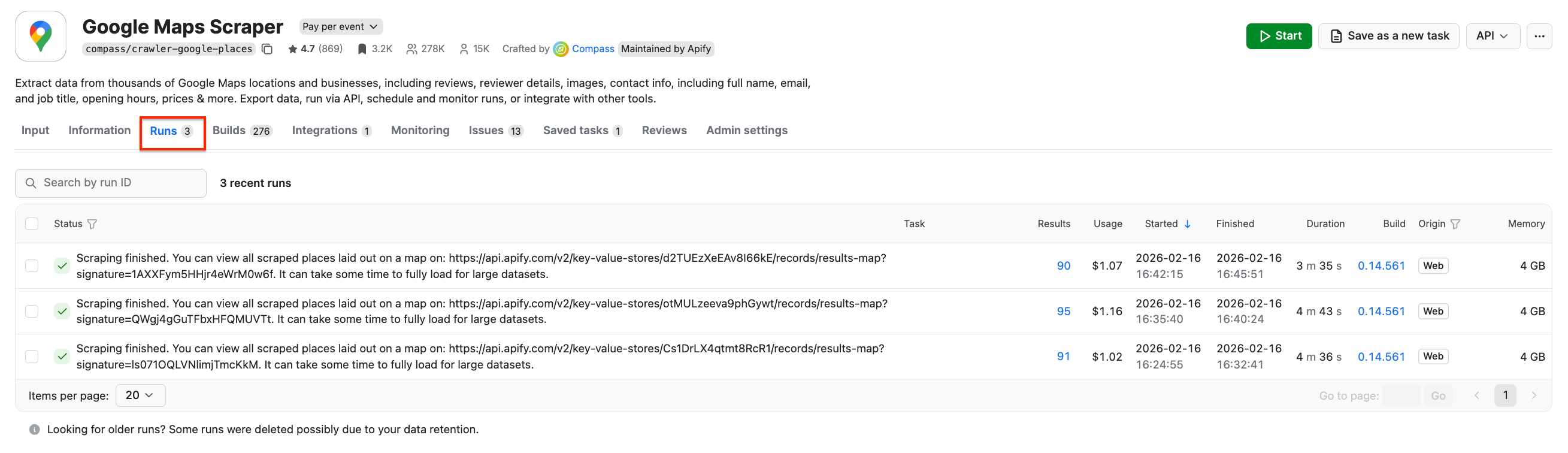
To access all your previous runs, select the Runs tab on the Actor page. Here you can always access your datasets and download them again if needed. Let’s download the results in JSON for each city.
Next, upload all three files to ChatGPT and Claude and use the models to analyze demand, competition, and population signals. Examples of prompts:
- ChatGPT prompt:
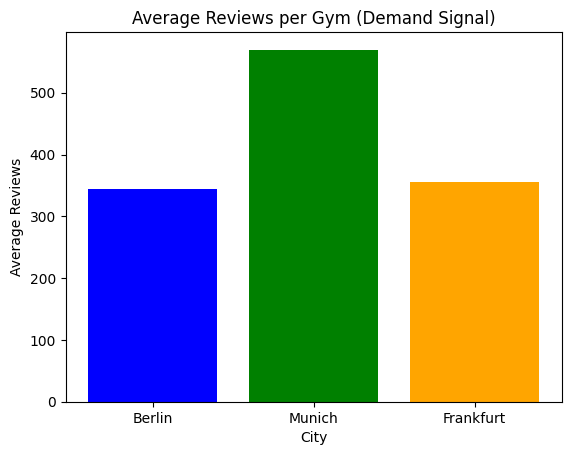
Analyze engagement and consumer demand in all three cities based on the number of gyms and reviews data
Result:
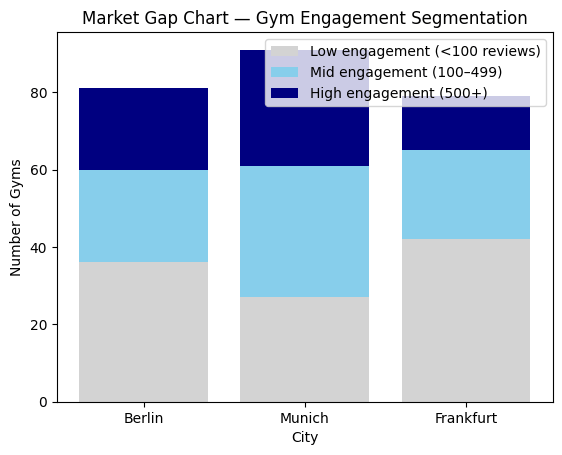

- Claude prompt:
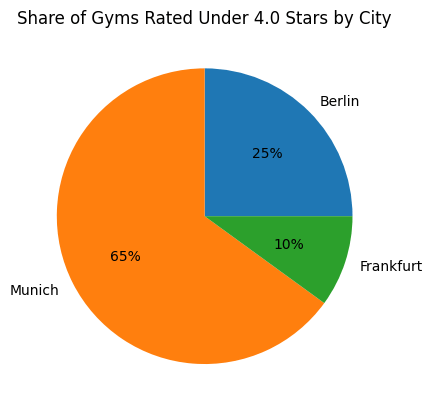
Examine the market size and density. Create a market opportunity scorecard taking into account market saturation, pricing, consumer satisfaction, and other factors.
Result:
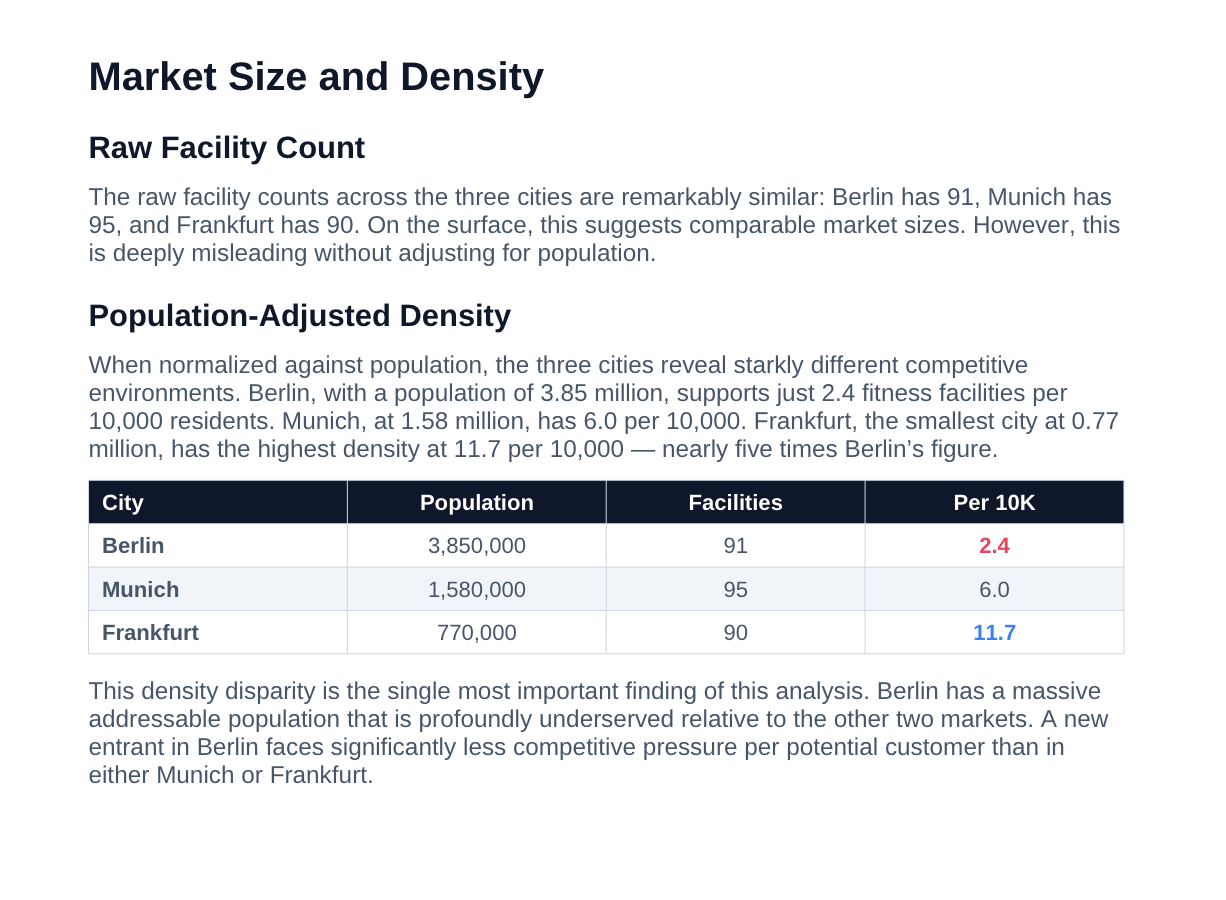
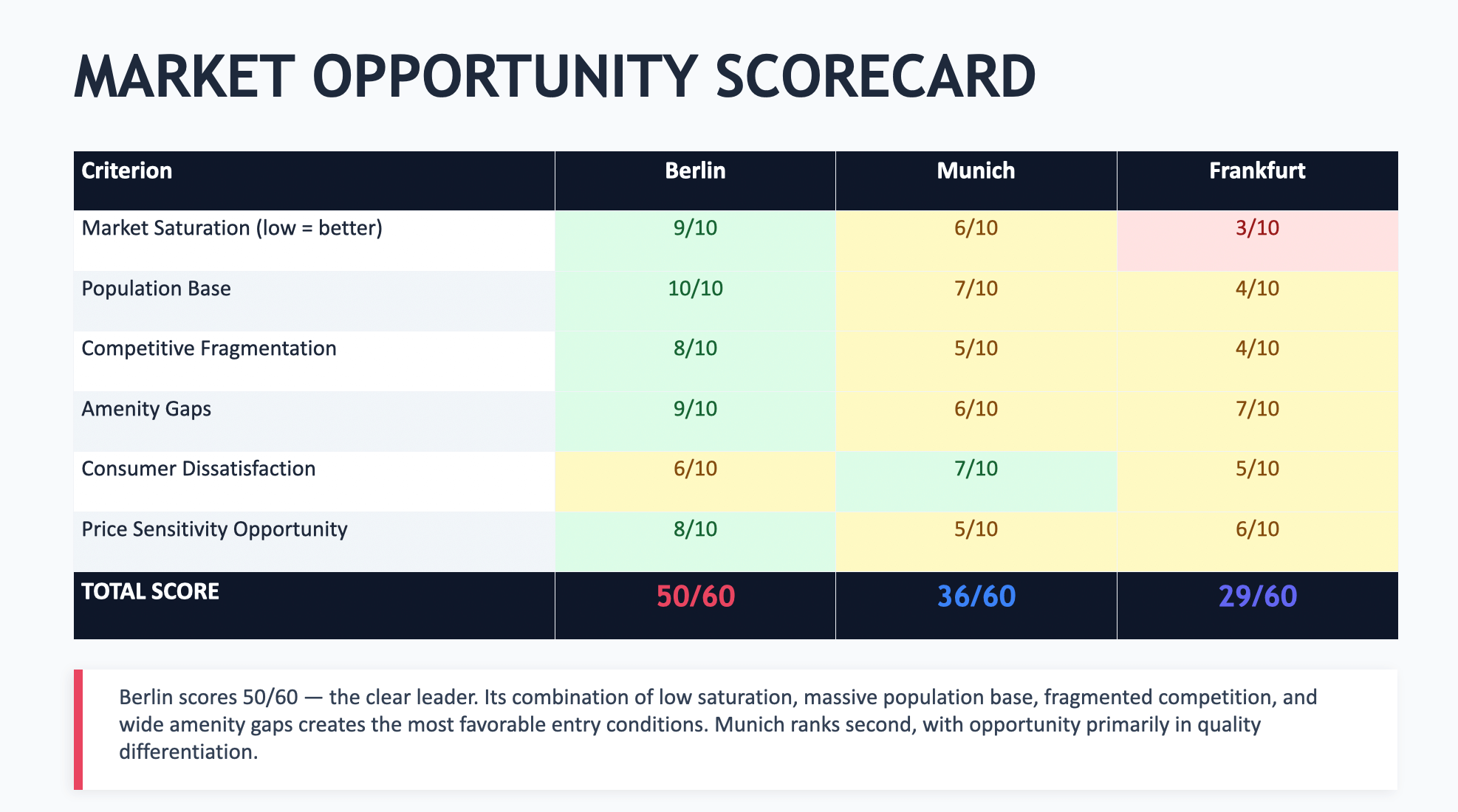
As you can see, Google Maps Scraper provides sufficient datasets to conduct a robust market expansion analysis - giving you clear visibility into competition, demand patterns, and expansion opportunities across cities.
Conclusion
Google Maps is one of the richest sources of local business intelligence available, but its manual limitations make it impractical for serious market research. By combining Google Maps Scraper with AI analysis tools, you can turn raw listings into expansion strategies - complete with density comparisons, competitive landscape mapping, consumer sentiment analysis, and opportunity scoring. You can achieve all that in a fraction of the time it would take to research manually.